The terms usability and user experience (UX) are often used synonymously. In fact, they are related but not identical concepts. In the following, we explain their similarities and differences.

BRIEFLY EXPLAINED
Usability, also called ease of use, is a result of the interaction between specific users and a product, service or system and is defined by the components of effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction.
User experience is a broader concept that includes all of a person's perceptions and reactions before, during, or after using a product, service, or system. Usability is thus an important part of user experience.
Usability refers to the ability of a device or human-machine interface to be easily used or operated. Part 11 of the ISO 9241 standard "Ergonomics of human-system interaction" defines usability as "the extent to which a system, product, or service can be used by specific users in a specific context of use to achieve specific goals effectively, efficiently, and satisfactorily" (ISO 9241-11:2018).
Effectiveness refers to "the accuracy and completeness with which users achieve specific goals"; efficiency to "the resources in relation to the results achieved"; and satisfaction to "the extent to which the user's physical, cognitive, and emotional responses resulting from the use of a system, product, or service match user needs and user expectations" (ISO 9241-11:2018).
According to ISO 9241-210:2010, user experience describes the "combination of perceptions and reactions of a person resulting from the actual and/or expected use of a system, product or service." These user perceptions and reactions include "all emotions, perceptions, preferences, perceptions, well-being or discomfort, behaviors, and performance that occur before, during, and after use."
While usability typically considers goals of user groups, user experience is about individual goals, which include personal motivations, such as the need to acquire new knowledge and new skills, to express one's personal identity, and to create positive memories.
Accordingly, user experience emphasizes the importance of subjective reactions and emotional experiences. While usability encompasses the performance-related characteristics of effectiveness and efficiency, it additionally includes the characteristic of satisfaction, which is concerned with personal aspects of the interaction. An example of this is the principle of user engagement, which is defined as "The interactive system presents functions and information in an inviting and motivating manner, encouraging continuous interaction with the system" (ISO 9241-110:2020). So while usability is an important part of user experience, usability also contains aspects of user experience.
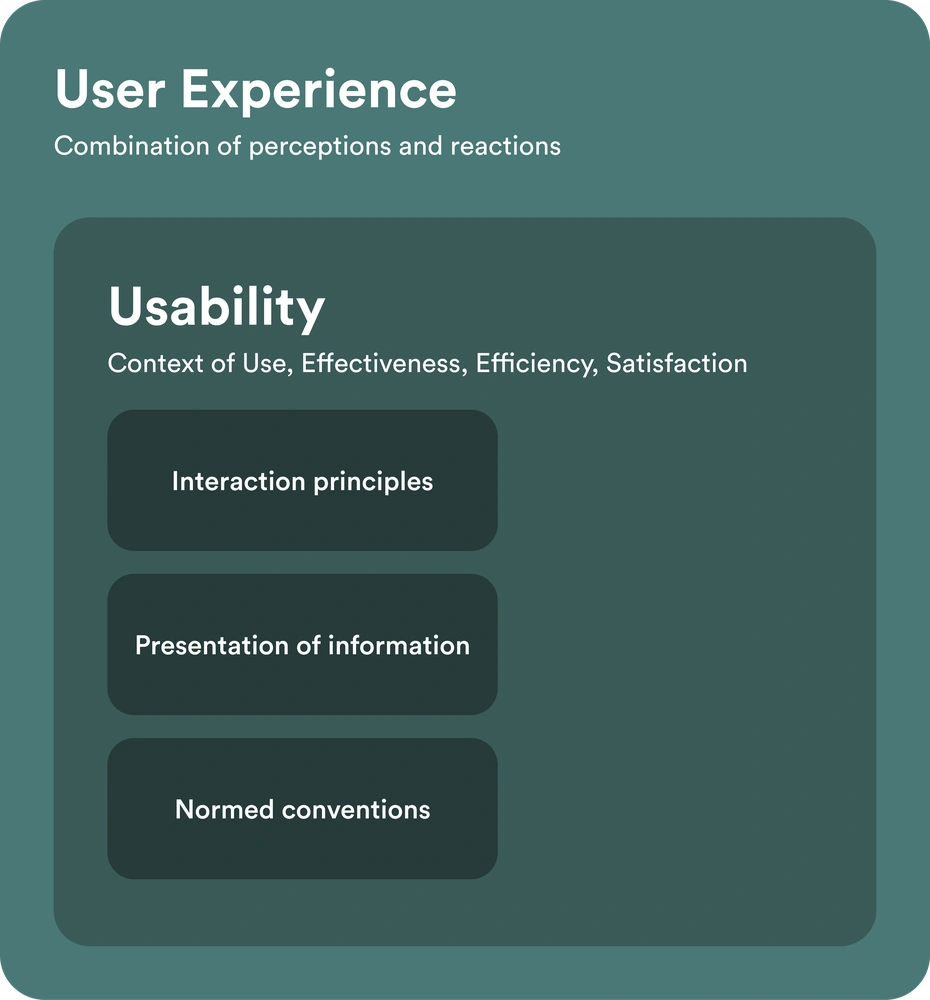
Part 110 of the ISO 9241 standard contains product-related principles and general design recommendations for the interaction between users and interactive systems that can be applied in the analysis, design, and evaluation of systems, products, and services. The goal of these principles and recommendations is to make user interfaces more usable, accessible, and consistent, and to enable higher productivity and a more positive user experience, as well as to prevent use-related harm.
Part 112 of the ISO 9241 standard contains ergonomic design principles of information presentation for interactive systems and is thus an important supplement to Part 110.
In addition to ISO standards, there are also standardized conventions that can be applied to improve usability and user experience, e.g. the Microsoft Windows User Experience Guidelines or the iOS Human Interface Guidelines.
Another concept that is often mentioned in connection with usability and for which there are separate standards is accessibility (German Barrierefreiheit, sometimes also Zugänglichkeit). Accessibility refers to the "extent to which products, systems, services, environments, and facilities can be used by people from a population with the widest range of user needs, characteristics, and abilities to achieve identified goals in identified contexts of use" (ISO 9241-112:2017). In other words, accessibility is usability for a wide range of users.
The WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) is an international standard that defines accessibility requirements for web content. By taking these norms and standards into account, products and services can be designed to be accessible and usable for as many people as possible.
At Ergonomen, we place great emphasis on the consideration of norms and standards as well as the application of best practices. We are committed to providing our customers with products and services that are not only functional and fit for purpose, but also offer a positive user experience.
We have a wide range of methods at our disposal. Here are a few of the most important.
Bevan, N., Carter, J., & Harker, S. (2015). ISO 9241-11 Revised: What Have We Learnt About Usability Since 1998? In M. Kurosu (Hrsg.), Human-Computer Interaction: Design and Evaluation (Bd. 9169, S. 143–151). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20901-2_13
DIN EN ISO 9241-11:2018-11, Ergonomie der Mensch-System-Interaktion — Teil 11: Gebrauchstauglichkeit: Begriffe und Konzepte (ISO 9241-11:2018); Deutsche Fassung EN ISO 9241-11:2018
DIN EN ISO 9241-110:2020-10, Ergonomie der Mensch-System-Interaktion — Teil 110: Interaktionsprinzipien (ISO 9241-110:2020); Deutsche Fassung EN ISO 9241-110:2020
DIN EN ISO 9241-112:2017-08, Ergonomie der Mensch-System-Interaktion — Teil 112: Grundsätze der Informationsdarstellung (ISO 9241-112:2017); Deutsche Fassung EN_ISO_9241-112:2017
DIN EN ISO 9241-210:2020-03, Ergonomie der Mensch-System-Interaktion — Teil 210: Menschzentrierte Gestaltung interaktiver Systeme (ISO 9241-210:2019); Deutsche Fassung EN ISO 9241-210:2019